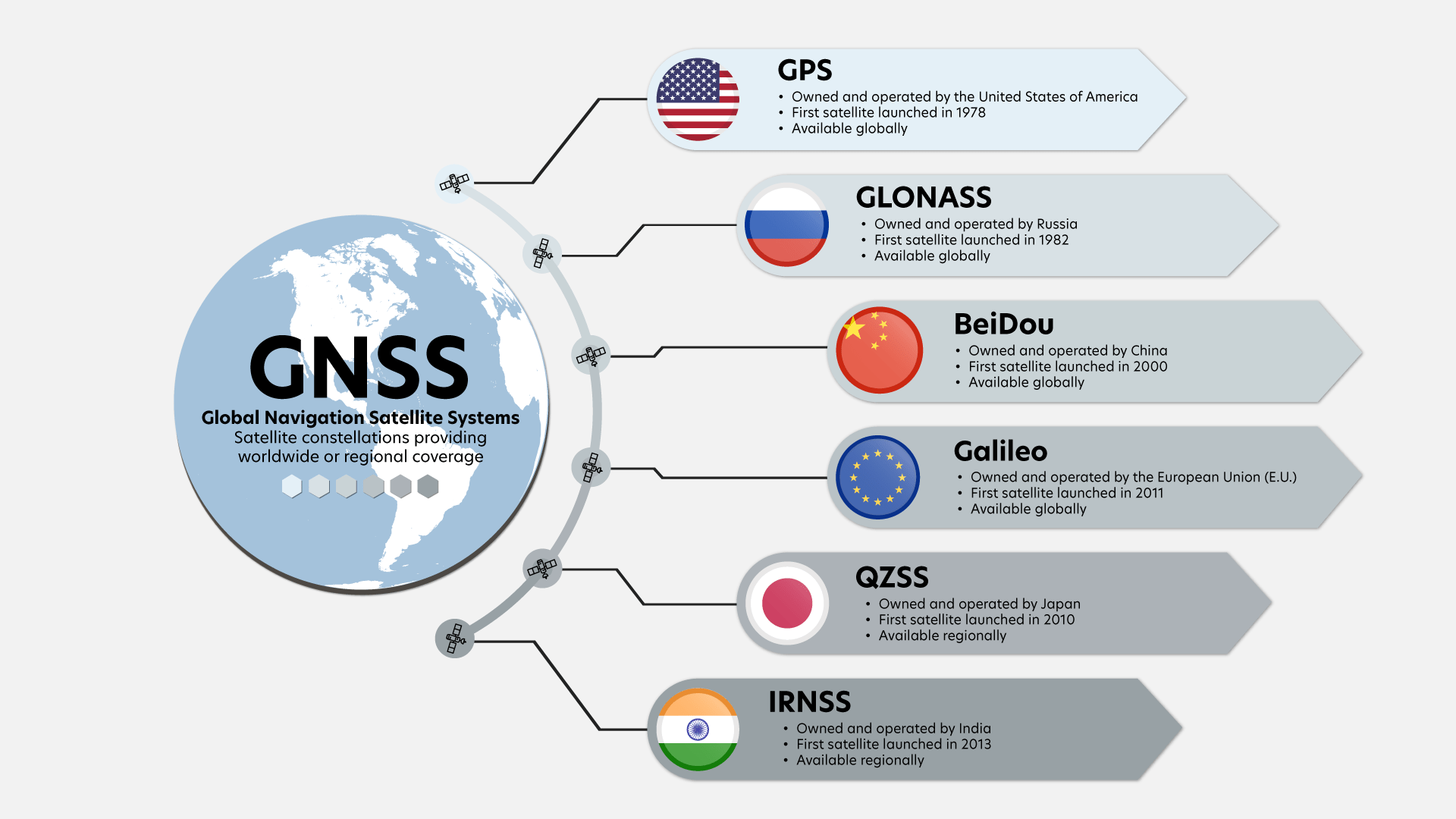
As India embraces GNSS-based toll collection to modernize its roadways, data privacy emerges as a key challenge. The technology’s potential to revolutionize toll collection with seamless and automated payment systems is exciting, but it also raises concerns about how location data is collected, stored, and used. Understanding these privacy challenges is essential to avoid the pitfalls of adopting such a system and ensuring that user data remains protected. Here’s a deeper look into the data privacy risks, practical solutions, and how stakeholders can tackle these issues.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Privacy Concerns: What’s at Stake?
Constant Surveillance and Real-Time Tracking
GNSS technology relies on continuous tracking of vehicles, making it possible to monitor a person’s travel patterns in real time. This level of detail could be exploited for surveillance purposes, potentially infringing on individuals’ privacy rights. There is a growing concern that misuse of this data could lead to tracking people’s movements without consent.
Data Security and Unauthorized Access
Securing the data collected from GNSS systems is paramount to prevent breaches. If this information falls into the wrong hands, it could be used for malicious activities, such as profiling, stalking, or even theft. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption and secure data storage, is essential to protect the integrity of user data.
Anonymization Gaps
While anonymizing data can alleviate privacy concerns, there are cases where anonymization techniques may not be sufficient. With advanced data analytics, even anonymized data can sometimes be re-identified, especially if combined with other data sources. The challenge lies in implementing techniques that effectively mask identity without compromising the usability of the data.
Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Use
Compliance with data protection regulations such as India’s Personal Data Protection Bill is crucial. It is not enough to secure the data; organizations must also ensure that data usage aligns with legal and ethical standards. This means using data only for the intended purpose and not sharing it with unauthorized third parties.
Transparency and Informed Consent
Users need to understand what data is being collected, how it is used, and whom it is shared with. Gaining explicit consent and providing options to opt out of certain data uses are necessary steps to maintain public trust in the system. Without transparency, there is a risk of eroding public confidence and facing legal repercussions.
Effective Data Anonymization: Protecting Privacy in Practice
To address these challenges, data anonymization must be implemented strategically. Here are the top techniques to enhance data privacy while still leveraging GNSS data effectively:
Data Masking
By replacing sensitive data elements with fictionalized or obfuscated values, data masking can hide original data details without compromising the dataset’s utility. For example, license plate numbers can be masked to ensure anonymity while still analyzing traffic patterns.
Generalization and Data Aggregation
Reducing the precision of data helps limit identifiability. Instead of exact locations, data can be aggregated to show vehicle movements across regions rather than pinpointing precise coordinates. This balances the need for useful data analysis with privacy protection.
K-Anonymity, L-Diversity, and T-Closeness
These techniques provide structured approaches to anonymization:
- K-Anonymity: Ensures each dataset record is indistinguishable from at least k-1 others.
- L-Diversity: Extends k-anonymity by ensuring the sensitive attribute has diverse values within each group.
- T-Closeness: Maintains that the distribution of sensitive data in a group is similar to its distribution across the entire dataset.
Differential Privacy
Adds noise to datasets, ensuring that individual records cannot be easily distinguished. This method is particularly valuable in statistical analysis and machine learning applications where aggregated insights are more important than individual data points.
Synthetic Data Generation
Creating artificial datasets that mimic the characteristics of real data without revealing actual personal information. This is useful for testing and analytics without exposing real-world data.
Implementing Robust Data Privacy Solutions
To effectively anonymize data and address privacy concerns in GNSS-based toll collection, organizations should adopt a comprehensive approach:
- Data Sensitivity Assessment: Identify which data elements pose the highest privacy risks.
- Layered Anonymization Techniques: Employ multiple anonymization methods to create stronger data protection.
- Ongoing Privacy Audits and Compliance Monitoring: Regularly review anonymization practices and update them according to the latest privacy standards.
- Clear Privacy Policies and User Agreements: Inform users about data collection practices, anonymization measures, and consent options to foster trust.
The Path Forward: Balancing Innovation with Privacy
While GNSS-based toll collection can significantly improve India’s road infrastructure, addressing data privacy concerns is crucial for its success. Transparent data practices, robust security measures, and effective anonymization techniques will help minimize risks and build public confidence in this advanced system. By staying vigilant about data privacy and implementing proactive measures, we can ensure that technological progress does not come at the expense of individual rights.

Jugaad on Two Wheels: The Hilarious Bike Parcel Hack in Karnataka
The Great Karnataka Bike Parcel Hack: A Jugaad Masterclass #RapidoParcel: In a creative yet controversial move, ride-hailing platform Rapido has found a way around Karnataka’s

Denmark’s Digital Sovereignty Revolution: Linux and LibreOffice Lead the Way
Introduction to Denmark’s Bold Move In June 2025, Denmark’s Ministry of Digital Affairs made headlines by embracing digital sovereignty, ditching Microsoft Windows and Office 365

🏏Sports as a Business Strategy: Insights from Vijay Mallya’s RCB Ownership
🧠 Sports as a Business Strategy (Tool) In modern business, few platforms offer better engagement and emotional connection than sports. From football clubs in Europe

🙏 Apologies in Leadership: Vijay Mallya Public Apology
🧠 Introduction: The Role of Apologies in Leadership In the corporate world, apologies aren’t signs of weakness—they’re strategic acts of leadership. When made with sincerity

Audiobook Production Costs: Navigating Recording Artists, Studio Expenses, and AI’s Impact
The audiobook industry is booming, with over 130 million listeners in the U.S. alone in 2021 and a growing global appetite for audio content. Producing

Media Trial of Vijay Mallya: How Public Perception Shaped Vijay Mallya’s Legacy
Introduction: Media’s Influence on Business Narratives In today’s hyper-connected world, media narratives can make or break a business reputation. For Vijay Mallya, once known as

1 thought on “Addressing Data Privacy Concerns in GNSS-Based Toll Collection: What You Need to Know”